What is aspartame?
Aspartame, also known as Acesulfame Potassium (E 951) is an artificial sweetener. It is sold under such brand names as NutraSweet, Spoonful or Equal. The artificial sweetener is a combination of amino acids: phenylalanine and aspartic acid.
When aspartame is broken down by the body, a part of it is broken down to methanol. It is used in producing many different foods and drinks. Aspartame is 200 times sweeter than sugar therefore it is required in much lower amounts than sugar, to reach the same level of sweetness.
Most of the products that are labeled sugar-free contain artificial sweeteners, such as aspartame. These products include soda, cereal, fruit juice, yogurt and many other types of food[1,2].
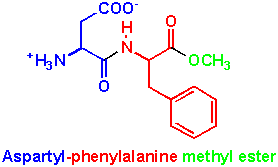
Aspartame in the body
When the body processes Aspartame, it is broken down into phenylalanine, aspartic acid and methanol. Phenylalanine and aspartic acid are amino acids that are normally present in many different foods. Foods high in phenylalanine are seeds and nuts, dairy, lean meat, eggs, beans and whole grains. Aspartic acid is present in poultry and meat, eggs and dairy and many other products.
It has been recommended by the Food and Drug Administration that the daily intake of Aspartame should not exceed 50mg/kg/day, whereas European Food Safety Authority recommended intake is not more than 40mg/kg/day. Exceeding these amounts of Aspartame might lead to health concerns. For example- a can of diet soda contains around 180 mg of aspartame. A 68kg adult would have to drink 15 to 18 cans of soda in one day to exceed the recommended amount. Also, to cause long term effects it should be done every day[1,2].
![]() Brand name of Aspartame i.e Equal
Brand name of Aspartame i.e Equal
Does aspartame cause cancer?
Scientists have conducted many studies to investigate the link between aspartame and cancer. In studies done on laboratory animals, daily dose of 4000mg/kg was given to animals over their lifetime. Some of these studies suggested, that aspartame increases the risk of blood cancer in rats, like leukemia (see acute lymphocytic leukemia) and lymphoma. In human studies, however, aspartame has not been found to cause cancer [3]. Byproduct of aspartame-methanol can cause liver cirrhosis and is a risk factor for liver cancer. Still, the dose that is ingested by using aspartame is not likely to cause cancer.
Aspartame controversy
In recent years there has been a lot of talk about the negative side effects of Aspartame and its ability to cause long term health problems. The first studies were carried out in 1996, when Aspartame was linked to increased risk of brain cancer, such as glioma.
This study did not have sufficient scientific basis to prove the actual link to aspartame causing brain cancer [6]. Another series of studies suggested that aspartame increases the risk of leukemia (see acute myeloid leukemia) and lymphoma (see non-Hodkins lymphoma) in rats therefore suggesting its negative effects in humans.
In 2013 European Food Safety Authority reviewed all the evidence on toxicity of Aspartame and concluded, that it is safe to use for everyone, including pregnant woman and children. The acceptable daily intake of aspartame is 40mg/kg of body mass per day[4]. This amount of aspartame is not likely to cause any type of cancer. Still, persons who intake aspartame, in comparison with no intake, has a higher risk of being overweight and developing type 2 diabetes [5].
Phenylketonuria and aspartame
Phenylketonuria is a rare metabolic disorder that is present at birth. PKU is present in one in every 10,000 newborns. Screening for PKU is usually done after the birth. The disease is caused by mutation in PAH gene, which encodes the production of enzyme- phenylalanine hydroxylase. In PKU the amino acid phenylalanine from diet is not processed and accumulates in the body. Increased levels of phenylalanine cause disturbances in brain development. Screening for this disease is very important, because using special, phenylalanine free diet can significantly improve the outcome (also read about cancer fighting foods).
People suffering from PKU have to be extra cautious about ingesting products containing aspartame, since one of its compounds is phenylalanine. It is especially important for children, who´s brains are still developing[7].

![]()
If you enjoyed this article, share it on social media. Share your personal experience in the comments box below.
References
- What is aspartame: http://www.healthline.com/health/aspartame-side-effects#Alternatives6
- Patient information about aspartame and its effects: http://www.cancer.org/cancer/cancercauses/othercarcinogens/athome/aspartame
- European Food Safety Authority on aspartame: https://www.efsa.europa.eu/en/topics/topic/aspartame
- EFSA study on aspartame and its health risks: http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.2903/j.efsa.2013.3496/epdf
- Aspartame in diet: https://dietandhealth.cancer.gov/docs/aspartame.pdf
- Study on aspartame linked with brain cancer: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8939194
- Aspartame and PKU: https://ghr.nlm.nih.gov/condition/phenylketonuria#
Similar Posts:
- Childhood Leukemia
- Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia
- Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia
- Acute Myeloid Leukemia
- Top 40 Cancer Fighting Foods
- Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia
- Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia







Leave a Reply