What is fibroid tumor?
Fibroid tumor or also known as uterine leiomyoma is a benign tumor of the uterus. These tumors result from overgrowth of smooth muscle in the uterus. In rare cases, benign leiomyoma can become malignant causing uterine sarcoma [1].
Causes of fibroid in women
The exact cause of fibroid tumor is not known, but the possible causes are believed to be:
- Genetic changes– the muscle cells of fibroids are different from the normal muscle cells of uterus
- Hormonal impact– estrogen and progesterone can promote the growth of fibroids. Normal muscle cells of uterus contain receptors for these hormones, but the abnormal cells have more receptors. For this reason after menopause the tumor may shrink.
- Growth factors
It is believed, that fibroid develops from one muscle cell. For some reasons this cell starts to rapidly divide, forming a firm muscular mass. There are some factors that increase the risk of developing a fibroid:
- Hereditary factors– very often is mother has had it, the daughter can also develop a fibroid
- Racial factors– African-American race is more likely to develop fibroids than other races and in an earlier age.
- Other risk factors:
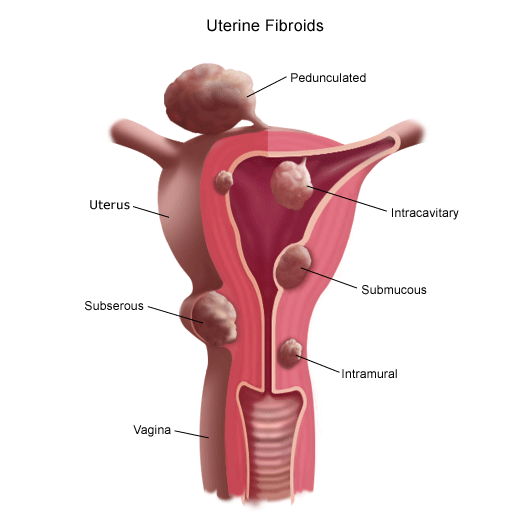
Types of fibroid
Fibroids can be divided in many different types based on their size, shape and location in uterus. Based on their location, fibroids can be divided in the following types:
- Submucosal- located under endometrium and extend into uterine cavity. Often cause heavy bleeding
- Intramural- found in the myometrium. Fibroids that are bigger in size can protrude into the uterine cavity or outside the uterus
- Subserosal- located under the outer lining or the uterus.
- Pedunculated- these fibroids are connected to the uterus with a tissue trunk. They can be located inside the uterine cavity or on the outside [3].
Symptoms
Fibroids are very common- it is estimated that up to 50% of women in reproductive age have them, but not all fibroids are diagnosed. Fibroids can be asymptomatic and sometimes they are found during ultrasound investigation. They can also cause symptoms:
- Irregular menstruations- cycle irregularity, heavy bleeding, bleeding in the middle of the cycle
- Pelvic pain due to compression of pelvic organs
- Lower back pain or leg pains
- Frequent urination or trouble emptying the bladder
- Dyspareunia- pain during sexual intercourse[3]
Diagnosis
Laboratory investigations
There are no specific laboratory investigations to diagnose fibroid tumor. Blood tests should be done to check for anemia- in some cases it can be caused because of heavy menstrual periods or bleeding in between periods [5]. Other causes of anemia should be excluded, like acute lymphocytic leukemia.
Imaging studies
Usually fibroids are found incidentally during pelvic examination. To make a complete diagnosis the following tests can be done:
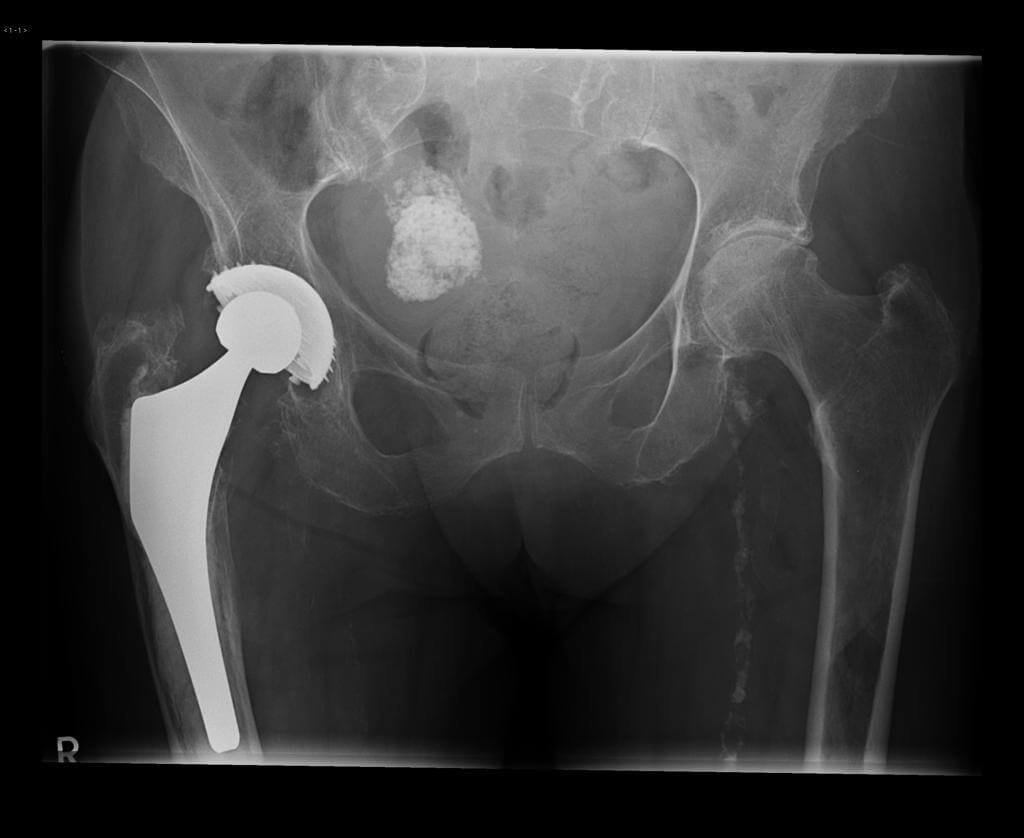
- X-ray- usually fibroids can´t be seen on X-ray examinations. In some cases when they are large in size, on plain X-ray fibroids can be seen as a mass of soft tissue that displaces intestines. Fibroids can also be heavily calcified, in which case they can be seen on X-ray.
![]()
- CT- computed tomography is limited, because fibroids can´t be distinguished from normal myometrium. In cases when the fibroid is calcified or necrotic, they can be diagnosed with CT.
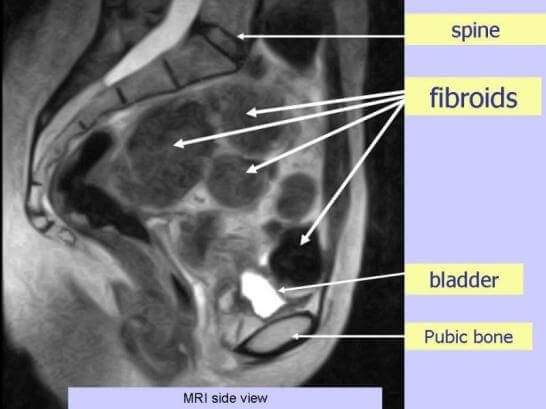
- MRI- magnetic resonance has an important role in diagnosing fibroids and planning their treatment. With MRI the exact location and size of the fibroid tumor. If contrast substance is used, fibroids usually have enhanced signal.
![]() Ultrasonography- method of choice when diagnosing fibroids. In ultrasound imaging fibroids appear as solid, well marked masses [4].
Ultrasonography- method of choice when diagnosing fibroids. In ultrasound imaging fibroids appear as solid, well marked masses [4].
Treatment
Medical
Medications
Fibroid tumors can be treated by using medications:
- Gonadotropin-releasing hormone antagonists- this medication causes a temporary menopausal state, during which the fibroid can shrink in size. Usually after stopping the therapy, fibroid grows back in its size and symptoms return
- Progestins, combined oral contraceptives, anti-estrogens can be used to control heavy bleeding. These medications only help the symptoms but they don’t treat the underlying cause
- Pain killers can be used to treat discomfort and pain caused by fibroids [5]
Other procedures
- Uterine artery embolization/fibroid embolization- during this procedure, the uterine artery is embolized blocking the blood flow to the fibroid. That leads to necrosis of the tumor.
- Magnetic resonance guided focused ultrasound- uses ultrasound energy to destroy the fibroid by applying heat.
- Endometrial ablation- used for treating small submucosal fibroids [5]
Surgical treatment
- Myomectomy– during this procedure, fibroid tumors are removed leaving the uterus intact. This procedure is best for women in reproductive age who still plan to have children. In some cases fibroids can recur. There are different methods that can be used to remove fibroids:
- Hysteroscopic myomectomy- used for removing submucosal fibroids by approaching them through vagina and cervix with a small camera.
- Laparoscopic myomectomy- used for removing intramural, subserosal or pedunculed fibroids.
- Open myomectomy- fibroids are removed by using a large abdominal incision.
- Hysterectomy– during this procedure the uterus is removed (also read fallopian tube cancer, choriocarcinoma) [5].

 Complications
Complications
One of the most common complications of fibroids is anemia, due to irregular and heavy bleeding. Symptoms of anemia are:
- Fatigue
- Trouble concentrating
- Paleness
- Headaches
- Increased heart rate
- Shortness of breath
Fibroids can also affect fertility and pregnancy. Usually submucosal fibroids or one´s that are large in size (>6cm) can affect chances of getting pregnant. The reasons why fibroids affect fertility are:
- They can change the shape of cervix, which affects how much sperm gets in the uterus
- They can change the shape of uterus, affecting the movement of sperm or the fertilized egg
- In some cases fibroids block fallopian tubes
- They can affect the blood flow in uterus, decreasing the ability for an embryo to implant in the uterine wall and later for it to develop
- They can increase the risk of preterm birth or miscarriage
- They can cause pain and affect the position of the fetus in uterus
Treatment of fibroids can cause infertility- usually pregnancy is not possible after ablation. Medications can also have an impact on cancer risk. For example, hormone therapy can increase the risk of breast cancer and endometrial cancer. But women using hormone therapy have a lower risk of developing colon cancer. [6]
If you found this article helpful, share it on social media. For your comments and personal experience use the comments section below.
References
- General information about fibroids: http://obgyn.ucla.edu/fibroids
- Causes and risk factors: http://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/uterine-fibroids/symptoms-causes/dxc-20212514
- Symptoms: http://www.uterine-fibroids.org/about-uterine-fibroids/
- Imaging of fibroid tumors: http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/405676-overview
- Treatment of fibroid tumors: http://www.nwh.org/departments-and-services/migs/conditions-treated/fibroids/
- Complications: http://www.reproductivefacts.org/FACTSHEET_Fibroids_and_Fertility/
Similar Posts:
- Choriocarcinoma – Symptoms, Prognosis, Treatment, Diagnosis
- Partial Molar Pregnancy – Pictures, Symptoms, Treatment
- Pituitary Gland Tumor
- Inoperable Brain Tumor
- Brenner Tumor
- Rhabdoid Tumor
- Granular Cell Tumor






Leave a Reply