What is laryngeal cancer?
Generally, laryngeal cancer is a type of neck and head cancer. It is also known as laryngeal carcinoma or cancer of the larynx. It is a medical condition wherein there is an abnormal growth of cells affecting the larynx (the voice box located at the throat’s back). The larynx, a vital organ, plays three important roles which aid in breathing, talking, and swallowing of food. Anatomically speaking, there are three parts of the larynx: subglottis, glottis, and supraglottis. The cancer can start to grow anywhere in these parts.
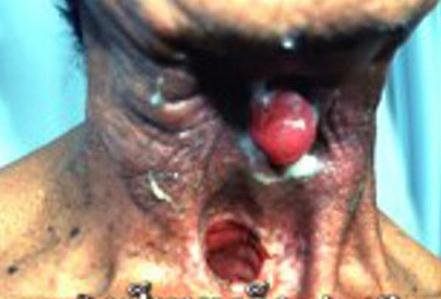 Laryngeal cancer symptoms
Laryngeal cancer symptoms
People with laryngeal cancer will experience some or all of the following symptoms:
- Pain in the neck
- Unintentional weight loss
- Dyspnea (difficulty in breathing)
- Enlarged cervical lymph nodes
- Difficulty in swallowing
- Persistent cough
- Changes in breathing sounds
- Hoarseness
- Bad breath
- Swelling of the neck
- Pain in the ear
Laryngeal cancer causes and risk factors
Risk factor is a medical term that refers to the chance of acquiring this kind of medical condition. The following are the risk factors and the causes which will bring about the occurrence of this kind of disease condition:
Poor nutrition – Poor nutrition can contribute to the high risk of laryngeal cancer.
Heavy alcoholic consumption – According to studies, heavy drinkers of alcohol have a higher chance of laryngeal cancer.
Smoking – Smoking, particularly the use of tobacco, can lead to the acquisition of neck and head cancer such as laryngeal cancer.
Genes – Some people with mutations in certain genes have an increased risk of laryngeal cancer.
Weak immune system – People with weak immune systems are susceptible to different kinds of diseases such as laryngeal cancer.
Human papilloma virus infection – The human papilloma virus can cause a variety of cancers that affect the reproductive organs and throat.
Race – Laryngeal cancer is most common among African Americans.
Age – Generally, laryngeal cancer mainly affects people aged 65 years and older.
Gender – Laryngeal cancer is more common in men.
Gastroesophageal reflux disease – This is a type of disease wherein the acid coming from one’s stomach regurgitates or returns to the esophagus. Studies have linked this medical condition to laryngeal cancer.
Laryngeal cancer pathophysiology
Laryngeal cancer can be basically classified as either intrinsic or extrinsic. The intrinsic type is found in the true vocal cords or the glottis area and does not have the ability to spread elsewhere, while the extrinsic type spreads early and can be located in the other regions of the larynx.
Laryngeal cancer stages
Generally, there are four stages of laryngeal cancer which are classified as Stage I, Stage II, Stage III, and Stage IV. In Stage I, the tumor is present in only one part of the laryngeal area. In Stage II, the cancer is present in the areas within the larynx. In Stage III, the cancer has already spread and has affected the lymph nodes. Stage IV is the last stage wherein the cancer has already spread to the body tissues outside the laryngeal region.
Laryngeal cancer treatment
The goal of laryngeal cancer treatment is to remove the cancer and prevent it from spreading to other parts of the body. The basic treatment management of laryngeal cancer deals with surgery, radiotherapy, and chemotherapy. Surgery deals with the removal of the tumor, radiotherapy focuses on the use of radiation to kill the cancer cells, and chemotherapy deals with the use of cancer toxic medications to eradicate and prevent further spread of the cancerous cells.
Laryngeal cancer prognosis and survival rate
If the laryngeal cancer is detected early, then the prognosis is favorable and the expected survival rate is high, compared to a late detection where the prognosis and survival rate are poor.
ICD 9 Code for laryngeal cancer
The ICD 9 code is a medical coding that is used by medical practitioners to determine the source or origin of cancer. When a person is diagnosed with laryngeal cancer, he or she will have an ICD 9 code of 161.9.
Similar Posts:
- Follicular Thyroid Cancer – Symptoms, Survival Rate, Prognosis
- Tongue Cancer Pictures, Symptoms, Treatment, Prognosis, Survival Rate
- Pituitary Gland Tumor
- Tonsil Cancer – Pictures, Symptoms, Survival Rate, Staging, Prognosis
- Gum Cancer – Pictures, Symptoms, Signs, Treatment, Complications
- Lip Cancer
- Pancoast Tumor – Symptoms, Treatment, Survival Rate and Prognosis






I always experience hoarseness of voice after some time of talking. I am a university professor so I can not go without talking for longer periods in a day. Can using the voice in this manner contribute to the development of laryngeal cancer? What steps do I need to employ to prevent such? Thank you.
Hi Lina! I always meet patients with concerns like yours. Although talking regulatory because of your profession may strain your larynx often, it will not lead to laryngeal cancer if and only if you take precautionary measures such as drinking lukewarm water to soothe the throat, avoiding smoking, alcohol and avoiding infection. You should also make sure to stay away from too much sweets and cold foods or beverages after you have your lectures to avoid spasms on the voice box and throat. Hope this helps.
Hi,I noticed a lump on my throat (onset 7 months ago) family doctor, had said it was the rings of the trachea. But two days ago I experienced Sore throat that is now gone, also, transient hoarse voice (1 day), now gone. I am afraid that these are beginning signs of laryngeal Cancer. Plus I’m on my 21st week of pregnancy. The ENT ordered an MRI but I’m afraid for the baby. What should I do?