What is Lip Cancer?
Lip cancer is a malignancy that results from the autonomous and uncontrolled cell growth in the lips. Lip cancer is a part of head and neck cancers and may occur together with oral cancer or maybe one symptom of oral cancer. Lip cancers come in the form of squamous cell carcinoma, the abnormal growth of the flat cells on the lips.
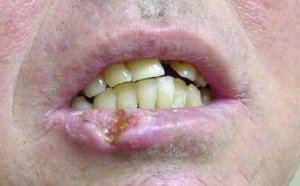
Ulceration of Lower Lip (Sign of Lip Cancer)
Lip cancers may be asymptomatic early in the progression of the disease. Malignant cells usually develop on the lower lip, rarely on the upper lip, but on some cases both are affected.
Also Read : Jaw Cancer – Symptoms, Pictures, Signs, Treatment, Prognosis
Lip cancer and oral cancer metastasize through the lymphatic system. The first metastatic area is in the lymph nodes of the neck and may spread to other distant organs in the body. As with oral cancers, lip cancers are predisposed by factors affecting the mouth. Up to 15% of oral cancers are lip cancer in origin. Lip cancer is responsible for about 4,000 cases of oral cancer yearly.
Symptoms & Signs
Clinical manifestations of lip cancer primarily involve the lips, but can also occur on adjacent areas in the mouth. The early stage of lip cancer may be asymptomatic. Symptoms of lip cancer include:
- A sore on the lip that does not heal
- Bleeding on the lip
- Lump on the lip
- Lip thickening
- Discoloration around the lip area or on the lip itself
- Lymphadenopathy or enlarged lymph nodes on the neck
- Swelling on the area
- Pain on the lip
- Tingling sensation or numbness on the lip
When lip cancer occurs with overall oral cancer, there may also be lesions inside the mouth or oral cavity that do not heal. Lesions may also spread on the throat or pharynx.
Also read : Gum Cancer – Pictures, Symptoms, Signs, Treatment, Complications
Causes & Risk Factors
The exact cause of cancers is unknown, but certain risk factors are associated with specific types of cancer. The risk factors for lip cancer are synonymous to the risk factors of oral cancer. These include:
Smoking and Tobacco Use
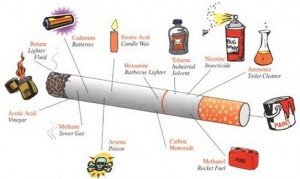
Smoking and tobacco has been the most often associated factor for lip and oral cancers. Cigarettes contain various carcinogens including tar. The chemical substances found in cigarettes damages the lining of the lip, which causes abnormal cells to proliferate. Almost all patients who suffered from lip cancer are smokers.
The Vast Chemicals of Cigarette Causes Lip Cancer
Alcohol Intake
The intake of alcohol leads to the penetration of DNA-damaging substances in the cells of the lip and mouth. When alcohol is paired by smoking, there is higher risk for the development of lip cancer.
Sun exposure
Exposure to the harmful ultraviolet radiation from the sun in prolonged periods can cause skin cancers, including lip cancer.
Infection with HPV
Warts caused by HPV (Human Papilloma Virus) can contribute to the development of lip cancer. HPV commonly affects the vagina, penis and cervix. The practice of certain sexual practices contributes to the spread of the virus in the lips and oral cavity.
Chronic irritation
Irritations on the lip caused by poor fitting dentures and other dental appliances may cause changes on the cells on the mouth and lips.
Lack of vegetables & fruits
These foods have antioxidant properties and it is thought that a lack of these in the diet may predispose someone to have lip cancer.
Male gender
Males have higher percentage of smokers and alcoholic drinkers, which predisposes the male population to oral cancers.
Above 40 years in age
Adults who have reached the age of 40 have higher risk because of more exposure to carcinogens and ultraviolet rays.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of Lip cancer includes physical examination of the area, complete medical history and diagnostic procedures such as:
Histologic Examination
Sample tissues from the lip tumor are taken and subjected to biopsy. Biopsy has been the only diagnostic tests to determine and confirm whether a tumor is malignant or benign. Histologic exams reveal squamous cell carcinoma of the lips.
Other tests for oral cancer may also be employed to determine presence of metastasis. Imaging tests such as MRI or CT-scan are used to assess distant metastases. Physical examination of the oral cavity and lymph nodes are also done to check presence of lesions in the mouth and lymph node enlargement.
The diagnosis of lip cancer is essential for staging to determine the best treatment regimen for the patient.
Staging
The staging of lip cancer is based on the staging of oral cancer in regard to spread which includes:
Stage I
Stage I lip cancer involves the growth of lip tumor, which is less than 2 cm in size. This stage does not involve lymph node spread yet.
Stage II
The tumor on the lip is more than 2 cm, but less than 4 cm in size. Still, there is no lymph node spread yet. Stage I and II are early stages and diagnosis this stage helps treatment to work.
Stage III
Stage III lip cancer involves two developments. Either the tumor is more than 4 cm in size with no lymph node affectation or the tumor is less than 4 cm in size, but there is already spread to one lymph node. Tumors that have spread on the lymph node are less than 3 cm in size.
Stage IV
The last stage of lip cancer involves spread of the lip tumor to the oral cavity and other adjacent tissues. There is also lymph node affectation of more than one lymph node which may vary in size. There is also distant metastasis to other parts of the body.
Another way of staging lip cancers is through the TNM staging system. In TNM staging, T stands for tumor; N stands for Lymph nodes and M for distant metastasis.
Tumor
- TX- This stage describes that the primary tumor cannot be assessed yet
- T0- There is no indication of primary tumor
- Tis- Stands for carcinoma in situ
- T1- Less than 2 cm diameter of tumor
- T2- Tumor is 2cm to 4 cm in size
- T3- Tumor size is more than 4 cm with spread to adjacent superficial tissues such as the tongue, sinus, etc.
- T4- Tumor spreads to the deep tissues of other organs in the oral cavity or other adjacent structures.
Lymph nodes
- NX- This stage describes that the regional lymph nodes cannot be assessed
- N0- No metastasis to lymph nodes
- N1- With metastasis to only one lymph node with 3 cm or less in size
- N2- Metastasis to one or more lymph nodes not more than 6 cm in size
- N3 Metastasis to lymph nodes with more than 6 cm in size
Metastasis
- MX- Distant metastasis cannot be assessed yet
- M0- There is no distant metastasis
- M1- With distant metastasis
Treatment
Treatment for lip cancer follows the most common management for all types of cancers including surgery, chemotherapy and radiation.
Surgery
Surgery involves the removal of lip tumor and neck surgeries including removal of the lymph nodes. Surgery is also used to determine spread of the cancer cells. Other tissues in the neck may also be removed when they are already affected.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy is an adjunct to surgery to completely remove cancer cells from the circulation and prevent further spread. Cisplatin (Platinol) is commonly used. Other combination drugs may also be administered. The use of chemotherapy should be cautiously administered because this may potentially lead to bone marrow suppression. Side-effects include temporary hair loss, anorexia, nausea, vomiting, and weight loss.
Anti-emetic drugs may be given prior to the administration of chemotherapeutic drugs to reduce nausea and vomiting. Patients should also be placed in reverse isolation precaution to prevent infection brought about by bone marrow suppression.
Radiation
Radiation therapy is also employed to halt spread and growth of malignant cells.
Complementary Therapy
Complementary therapies may also be employed to increase the well-being of cancer patients. Most commonly employed therapy is acupuncture, yoga and massage therapy. These managements should not be done in place of medical interventions.
Hospital care
In cases of patients who have advanced progress of disease and did not respond to therapy, the alleviation of suffering is the primary goal. Pain should be minimized to ensure comfort and reach optimum level of functioning. Hospice care aside from pain alleviation, also involves spiritual and emotional care to the patient and support systems.
Prognosis and Survival Rate
Oral cancers and lip cancer are one of the most slowly progressing types of malignancies. Detecting lip cancer early have good prognosis. The five-year survival rate of lip cancer is as high as 75% especially during the early stages of the malignancy where lymph node affectation is not yet preset. As the disease progresses, the survival rate also decreases.
Also read : Tongue Cancer Pictures, Symptoms, Treatment, Prognosis, Survival Rate
Complications
Aside from metastases to other parts of the body, lip cancer also results in altered body image because of the presence of tumor on the lips. This significantly reduces the self-esteem of the patient. Metastasis to the oral cavity also yields difficulty in drinking, eating, talking or breathing.
Prevention
Preventing lip cancer involves avoiding the modifiable risk factors such as:
- Smoking cessation and stopping tobacco use
- Moderate consumption of alcohol beverages
- Avoiding unsafe sexual practices such as oral sex
- Avoid prolonged sun exposure especially between 10 am and 3 pm to prevent exposure to the harmful ultraviolet rays
- Wear sunscreen on the lips
- Include fruits and vegetable in the diet and consider taking vitamin supplements
References:
- http://www.cancercenter.com/oral-cancer/types/tab/lip-cancer/
- http://www.cancer.gov/types/head-and-neck/patient/lip-mouth-treatment-pdq
- http://www.colgate.com/en/us/oc/oral-health/conditions/cancer/article/lip-cancer-signs-0815
- https://www.healthgrades.com/conditions/lip-cancer
- www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3146335/
- www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/lip-cancer/basics/definition/con-20037119
- www.cancersupportcommunity.org/oral-and-lip-cancers
- med.uth.edu/orl/newsletter/lip-cancer/
- cancercompass.com/message-board/message/all,60414,0.htm
- www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/165331.php
- patient.info/health/mouth-oral-cancer
Similar Posts:
- Gum Cancer – Pictures, Symptoms, Signs, Treatment, Complications
- Jaw Cancer
- Tongue Cancer Pictures, Symptoms, Treatment, Prognosis, Survival Rate
- Medullary Thyroid Cancer – Symptoms, Treatment, Prognosis
- Vaginal Cancer – Symptoms, Signs, Pictures, Treatment, Causes
- Fallopian Tube Cancer – Symptoms, Prognosis, Survival Rate, Treatment
- Vulvar Cancer






i want know the treatment for lip cancer, when it’s in first stages ….and care take by the family of that patient ,,,,we want to know which foods & drugs are used for that kind of people….pl z reply for my question
I have a ball in my upper lip inside and when I press down it hurts and sometimes ichy.
thanks for your help i gladly appreciate e
very bit of your help.
I support blockers.