What is Follicular Thyroid Cancer?
Follicular thyroid cancer, which is a type of neoplasm involving the thyroid gland, resembles the normal thyroid in microscopic pattern. It originates from the follicular cells. It is otherwise known as follicular adenocarcinoma or follicular cancer. It is the second common type of neoplasm in the thyroid gland. It occurs most often in women above the age of 40 and especially those who have low intake of iodine. It is an aggressive kind of cancer, which rarely occurs in children. In addition, it is a differentiated thyroid cancer. Also, it is a noninvasive type of cancer, which may spread to nearby organs like the lungs, brain, skin, bladder or liver and bones.
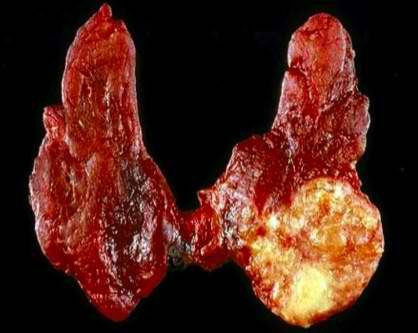
Follicular Thyroid Cancer
Symptoms
Some may have or may not have symptoms associated with follicular thyroid cancer. The symptoms associated with Follicular thyroid cancer are as follows:
- Swallowing difficulty
- Breathing difficulty
- Hoarseness
- Pain in the neck or throat sometimes it is painless
- Persistent cough
- Swollen neck glands
- Lump in the neck region
- Palpable nodules of the thyroid
Causes
Normally, the thyroid gland is sensitive to ionizing radiation effects which are a high risk for most thyroid cancer. Other etiological reasons include:
Genetics
Genetics play a role in the development of follicular thyroid cancer. Genetics are one of the high risk factors, which are seen through the form of having an abnormal oncogene and a family history of either goiters or precancerous polyps.
Gender
As mentioned earlier, this type of follicular thyroid cancer statistically happens mostly in women.
Age
Persons of the age of 40 years or above have been known to acquire this type of thyroid cancer.
Deficient Iodine in diet
Having a low iodine diet will put you at high risk for this type of cancer.
Exposure to radiation
Even moderate exposure to radiation may increase the risk of acquiring this form of cancer. Exposures to radiation via radioactive iodine, through the radiation therapy for lymphoma diseases and moderate to low dose x-rays are potential etiological factors.
Race
According to experts, Asians are more likely to develop this type of cancer. However, in general, it can affect anybody regardless the ethnicity or race.
Histology
The lesions demonstrate defined follicles and may possibly be encapsulated. It is distinct from other follicular adenoma due to the fact that it contains colloid. The diagnosis of follicular thyroid cancer is based upon the finding of blood vessel invasion and pseudocapsule. In addition, looking at a high magnification through the microscope may reveal abortive follicles demonstrating atypia of follicular type of epithelium. Abnormal and large thyrocytes can also be seen. Colloid follicles, which are lined by flat follicular cells may also be present. Lastly, the definitive diagnosis will be determined through the samples culled from the use of fine needle aspiration biopsy.
Treatment
The treatment of Follicular Thyroid Cancer deals with four options, which are surgical treatment, pharmacological treatment, radiation treatment and chemotherapy treatment. The following treatments will be discussed further.
Surgical Treatment
The primary treatment for follicular thyroid cancer is surgical treatment. The surgery will greatly depend on the extent of the disease condition. Surgery’s aim is to remove the neoplasm to prevent it from spreading to its nearby organs. The following common surgical procedure may be done:
- Subtotal thyroidectomy that deals with the removal of a portion of thyroid gland.
- Lobectomy with isthmectomy that deals with the removal of the nodule or isthmus which is a part of the thyroid gland.
- Total thyroidectomy that is the removal of the entire thyroid gland.
- Lymphectomy is the removal of the nearby affected lymph nodes.
Pharmacological Treatment
The next vital treatment option is the pharmacological treatment, which usually means thyroid hormonal replacement treatment. This usually follows after surgical procedure. It is done to maintain the normal level of thyroid hormones in the body. It is often given in high doses compared to persons who have no thyroid cancer.
Radiological Treatment
This treatment will aid in the removal or decrease the risk for recurrence of cancer as well as destruction of either the remnant ablation or the remaining cancerous thyroid cells. This is also done after surgical procedure. The common radiological treatments used are radioactive iodine therapy and external radiation therapy. The main difference between the two is that the radioactive iodine therapy is a pill that is taken internally.
Chemotherapy Treatment
Chemotherapy is another treatment used for persons suffering from this disease condition. It is a systemic type of therapy, which is delivered via the bloodstream to aid in the halting and destruction of the cancer cell progression. In addition, it also reduces the experience of pain. This is commonly done in persons who have severe or advanced cancer.
Prognosis & Survival Rate
Generally, the prognosis or survival rate of persons diagnosed with follicular thyroid cancer is good. This is a curable and manageable type of thyroid cancer. In addition, it has a good prognosis especially when the person is younger than 40 years of age, without vascular invasion or perhaps extracapsular extension of the thyroid cancer. The overall staging of follicular thyroid cancer is staged into I to IV. The chance of survival lowers as the person goes into the thyroid stages. However, it is impossible to predict the outcome of the individual person. The prognosis is based on variety of factors like response of treatment given, early diagnosis, which leads to good prognosis, age, gender and management of the disease condition. According to experts, there is a five to ten year survival rate for persons with follicular thyroid cancer that is based on cancer survival statistics. The cancer survival statistics should be cautiously interpreted; for this kind of statistic is being measured every interval of five years.
Similar Posts:
- Medullary Thyroid Cancer – Symptoms, Treatment, Prognosis
- Anaplastic Thyroid Cancer – Symptoms, Treatment, Prognosis
- Pituitary Gland Tumor
- Pineal Gland Tumor
- Tongue Cancer Pictures, Symptoms, Treatment, Prognosis, Survival Rate
- Acinic Cell Carcinoma
- Top 40 Cancer Fighting Foods






Leave a Reply