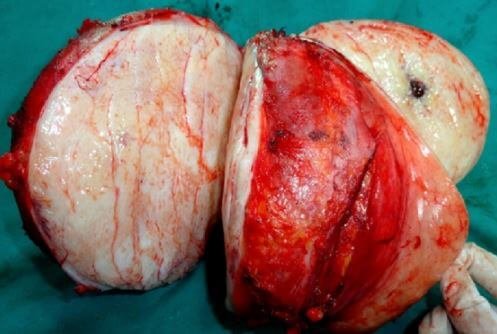
What is Desmoid Tumor?
Desmoid tumor is benign overgrowths that arise on connective tissues in the body. These tumors are noncancerous because they seldom spread to other parts of the body. However, some of these tumors are aggressive and are more likely to become cancerous. Aggressive tumors can spread to other parts of the body and cause serious complications1, 5.
Desmoid tumors can develop anywhere in your body and at any age. But women who are above 30 years are more likely to have these tumors. These tumors are not common because only less than four people in a million can have theses tumors.
Causes
The real causes of desmoid tumors are not yet known. However, these tumors are associated with the following:
Familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP)
It is a genetic condition in which potentially cancerous polyps develop in walls of the intestine. It occurs due to mutations in APC gene and can be passed from a parent to a child.
Symptoms
Signs and symptoms of a desmoid tumor depend on its location in the body. If the tumor is near to the surface of your skin, you may have a lump that is painless or slightly painful.
If the tumor occurs in your abdomen, it can compress blood vessels and veins causing pain. This may make you unable to use your leg, hand or arm. This tumor may grow and block your large intestine or spread to other tissues in your body. In the event that the tumor obstructs your colon, you will experience severe pain and bleeding in the rectum.
Diagnosis
A number of methods can be used to diagnose desmoid tumor. They include:
Physical examination
During this exam, your doctor examines the size of the tumor, its effect on the skin and the motion of nearby joints.
Ultrasound
It is also referred to as sonography and it involves the use of high sound waves to produce images of the inside of your body. In this method, the sonographer or ultrasound technician performs the test using a transducer which releases high frequency sound waves into your body.
As the sound waves passes through tissues and organs in your body, it produces echoes which are recorded by the transducer. This information is displayed on the computer screen in form of images and your doctor can help in interpreting the images. Ultrasound test is used to determine whether the tumor is solid or not.
MRI scan
This method involves the use of strong magnetic waves and radio waves to examine the inside of your body especially soft tissues and assist in assessing problems in these tissues. Your doctor conducts a MRI scan to assess the size and location of the tumor and whether it has spread to other parts of your body or not.
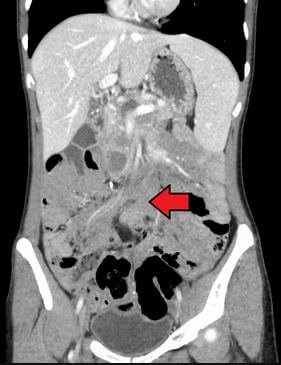
CT scan
This method uses X-rays to create many pictures of the tumor from different angles. Your doctor conducts this scan so as to assess the tumor from different angles.
Biopsy
This method involves removing a sample of a tissue and examining it under the microscope. In this procedure, your doctor will inject a local anesthetic near the tumor to numb the area and use a needle to remove a sample of the tumor. The sample is taken to a pathologist to examine whether the tumor is cancerous or not.
Treatment
Desmoid tumor is unpredictable; some of them grow rapidly and others remain the same after a diagnosis. This tumor can spontaneously decrease in size. These inconsistent behaviors of desmoid tumor make its treatment difficult.
Treatment of desmoid tumor depends on the location of the tumor, its characteristics and what the patient want. Several methods can be used to manage desmoid tumors such as nonsurgical and surgical methods.
Nonsurgical techniques
There are many nonsurgical techniques that have been used to treat desmoid tumors but they give mixed results. The following are some of nonsurgical treatment options:
Hormone therapy
Hormone estrogen stimulates the growth of desmoid tumor. Your doctor would recommend drugs that inhibit hormone estrogen from stimulating the tumor so as to control the growth of the tumor.
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
Your doctor can prescribe for you NSAIDs drugs such as ibuprofen to reduce pain and inflammation caused by the tumor.
Radiation therapy
This technique uses radiation to destroy cancerous cells and shrink the size of the tumors. Radiation therapy can be used alone or in combination with surgical technique so as to effectively treat the tumor. In case, radiation therapy is used together with surgery, it has to be done after two weeks the patient undergone surgical treatment.
Use of radiation therapy causes a number of undesirable side effects such as it may lead to joints becoming stiff, damages blood vessels supplying blood to the brain, it can lead to skin necrosis; a skin condition where cells in the skin are death. In some cases, radiation therapy may trigger the growth of other cancers in your body.
Chemotherapy
Your doctor may recommend low doses of chemotherapy drugs to manage desmoid tumors. These drugs cannot be used for a long time because they may negatively affect your overall health.
Radiofrequency ablation
In this method, your doctor uses high frequency electric current to heat and destroy the tumor. Alternatively, the doctor can directly inject irritating chemicals such as acetic acid to the tumor so as to manage it.
Surgical treatment
Surgery is the preferred method of treating desmoid tumors. However, surgery may be difficult if the tumor is in the abdomen. Desmoid tumor spreads to the limb’s nerves and blood vessels and its complete removal may affect the functioning of surrounding areas.
Therefore, other treatment methods such as chemotherapy and radiation can be used together with surgery to manage the tumor. This tumor may recur after surgery.
After you have go through any of the above treatment options, the time take for you to recovery full and resume normal activities depends on the location of the tumor and the extend of surgical methods.
In most cases, you will be recommended to a physical therapist who will teach you several exercises to strength your muscles. The main goal of this therapy is to help you regain motion in the affected limbs and joints. You will also continue to go for checkups after three months to help manage the tumor.
Reference List
- Desmoid tumor. http://www.webmd.com/colorectal-cancer/desmoid-tumors-facts#1
- Familial Adenomatous Polyposis. http://www.webmd.com/digestive-disorders/familial-adenomatous-polyposis
- Desmoid tumor. http://orthoinfo.aaos.org/topic.cfm?topic=A00505
- Familial Adenomatous Polyposis. http://www.cancer.net/cancer-types/familial-adenomatous-polyposis
- Desmoid tumor. http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1060887-overview
Similar Posts:
- Syringoma – Treatment, Removal, Pictures, Causes, Surgery, Prevention
- PNET Tumor
- Duodenal Cancer – Symptoms, Prognosis, Survival Rate and Treatment
- Amelanotic Melanoma – Pictures, Symptoms, Prognosis
- Morton’s Neuroma
- Dermatofibroma
- Sessile Polyp






Leave a Reply