Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Definition
Nasopharyngeal carcinoma which is also known as nasopharyngeal cancer is a type of cancer on the neck and head that rarely occurs, but it could affect both males and females. Knowing the structures and how the nasopharynx work will help an individual understand nasopharyngeal carcinoma.
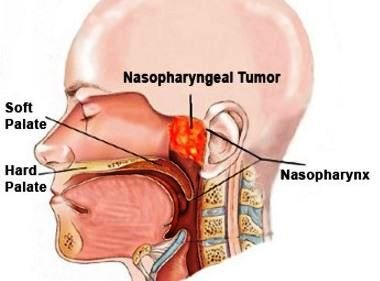
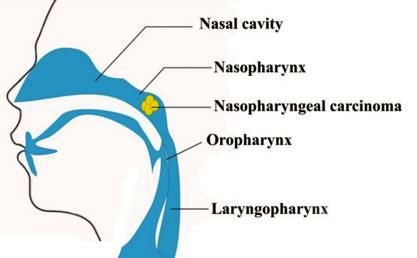
The cancer begins in the nasopharynx which is the upper area of the throat or pharynx just behind the nose. The nostrils directly lead to the nasopharynx as it is the passageway of air.
When a person breathes in, air gets into the nose and eventually reaches the lungs. This tumor is the most common tumor of the nasopharynx that is malignant. A carcinoma is a kind of cancer that begins in epithelial cells that line both the internal and external body surfaces.
Symptoms
Nasopharyngeal carcinoma does not result to any signs or symptoms in its early stages. Possible symptoms if problems occur are the following:
- Doubled or blurred vision
- Numbness of the face
- Trouble breathing
- Problems that concerns speech including hoarseness
- Headache
- Face pain
- Sore throat
- Nose bleeding
- Blood in the saliva
- Infections of the ear that keeps on recurring
- Lump in the nose or neck due to a swollen lymph node
- Stuffy nose
- Hearing loss
- Hearing issues such as a certain feeling of fullness inside the ear or ringing in the ears
A lot of the signs and symptoms of nasopharyngeal carcinoma are frequently caused by other diseases that are less serious. This does not mean that it is not a problem anymore. If any of these symptoms occur, see the physician right away for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Causes
Cancer itself starts with one or more DNA mutations that lead to normal cells to grow and invade other structures and metastasize to other areas of the body. The tumors in nasopharyngeal carcinomas start in the epithelial cells, but the gene mutations that exactly caused the cancer are not known.
However, there are factors such as the Epstein-Barr virus that could increase a person’s risk of having this cancer. It is still not clear why other individuals have most if not all of the risk factors but do not develop cancer, while some who have no obvious risk factors do.
Staging
TNM system is commonly used in describing the spread of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. This system involves:
- T: The primary tumor has occupied other organs or tissues near the nasopharynx.
- N: The cancer cells had spread to nearby lymph nodes.
- M: The cancer cells had metastasized or spread to other areas of the body.
Treatment
There are several ways of treating nasopharyngeal carcinoma which depends on the cancer stage, treatment goals, the patient’s health, and tolerance to side effects.
Standard treatments are the following:
Radiation therapy
It is the type of treatment that uses X-rays or other kinds of radiation to kill and get rid of cancer cells. For small tumors, this therapy alone may be the only treatment needed but in other circumstances, radiation therapy is combined with chemotherapy.
Chemotherapy
This kind of treatment makes use of drugs to prevent cancer cells from growing by either stopping it from dividing or killing the cells.
Surgery
Surgical treatment is a procedure performed by the physician in order to remove cancer cells from the body or to fix a body part. In the case of nasopharyngeal cancer, surgery is recommended when the patient does not respond to radiation therapy or if the cancer cells had spread to the lymph nodes.
New kinds of treatment options are put to test in clinical trials and these include:
Biological therapy
This is a treatment that makes use of the patient’s immune system to fight off cancer. Certain substances are used to boost or restore the natural defenses of the body towards cancer.
Intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT)
This is a 3-dimensional therapy that uses images that are computer-generated to visualize the shape and size of the tumor.
Survival Rate
5-year survival rates are the percentage of patients who survives for at least 5 years after their diagnosis although many live for a longer time or cured completely. Percentages are as follows:
- Stage I/T1/N0/M0 with tumor in nasopharynx: 72%
- Stage II/T2/ N0/M0 with tumor on sides of throat: 64%
- Stage III/T3/ N0-N2/M0 with tumor spread on sinuses or bones near pharynx: 62%
- Stage IV/T4/ N0-N2/M0 with tumor on skull or cranial nerves: 38%
References
- http://www.medicinenet.com/nasopharyngeal_cancer/article.htm#nasopharyngeal_cancer_is_a_disease_in_which_malignant_cancer_cells_form_in_the_tissues_of_the_nasopharynx
- http://www.cancer.org/cancer/nasopharyngealcancer/detailedguide/index
- http://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/nasopharyngeal-carcinoma/basics/definition/con-20025379
- Li JG, Yuan X, Zhang LL, Tang YQ, Liu L, Chen XD, et al (2013 Sep 1). A randomized clinical trial comparing prophylactic upper versus whole-neck irradiation in the treatment of patients with node-negative nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer. 119 (17):3170-6.
- Gu MF, Liu LZ, He LJ, Yuan WX, Zhang R, Luo GY, et al (2012 May 18) . Sequential chemoradiotherapy with gemcitabine and cisplatin for locoregionally advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Int J Cancer.
- Laskar S, Bahl G, Muckaden M, Pai SK, Gupta T, Banavali S, et al (2008 Nov 1). Nasopharyngeal carcinoma in children: comparison of conventional and intensity-modulated radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 72(3):728-36.
Similar Posts:
- Urothelial Carcinoma
- Acinic Cell Carcinoma
- Squamous Cell Carcinoma in Situ – Pictures, Treatment, Symptoms
- Tonsil Cancer – Pictures, Symptoms, Survival Rate, Staging, Prognosis
- Jaw Cancer
- Brenner Tumor
- Trichoepithelioma – Pictures, Treatment, Symptoms, Causes






Leave a Reply