Definition
Diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma abbreviated as DIPG is considered as a rare brain tumor that aggressively affects the pons region involving the brainstem and is responsible for a person’s vital signs like blood pressure, cardiac rate, and respirations.
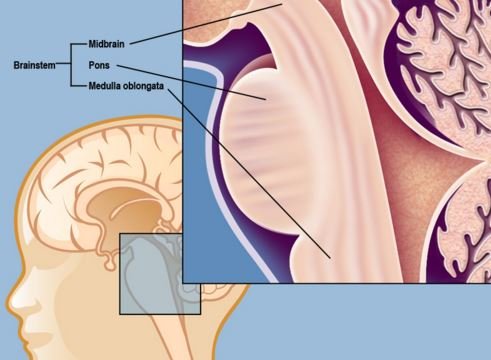
The brainstem significantly connects the cerebrum and the spinal cord. Most patients that are affected of this condition are usually children and are not common in adults. These tumors can rapidly spread anywhere else and they emerge from the glial tissues of the brain.
The tissues are composed of cells that aids in protecting and supporting the neurons or the thinking cells of the brain.
Many children are diagnosed of having DIPG tumors each year that commonly occurs between ages 5 and 9, although they could appear at any age during childhood. Both girls and boys have equal chances to have these tumors.
Symptoms of Diffuse Intrinsic Pontine Glioma
When the pons is affected by DIPG, it can greatly affect the tasks of the nervous system which leads to some symptoms that are quite difficult to handle.
Since pontine gliomas frequently influences the cranial nerves, the early symptoms commonly involves the facial muscles such as movements of the eyelids and the eye. The tumors are very aggressive that the symptoms appear on sudden occasions and get serious quickly.
Symptoms of DIPG include:
- Facial frailness in which one side of the face sags down
- Headache
- Eye movement problems such as problems of adjusting vision going to the side, eyelids may also droop, eyes not shut completely, and double vision
- Unexpected problems of hearing such as deafness
- Gagging while eating
- Vomiting and nausea due to hydrocephalus with an abnormal collection of cerebrospinal fluid in the brain
- Abnormal gaits
- Having the difficulty in swallowing or chewing
- Unstable limb movements
- Weakening of the limbs that makes walking or standing difficult
Causes of Diffuse Intrinsic Pontine Glioma
The scientists or other researches still do not know the exact causes of DIPG and in addition to that, the condition is very rare which only means that the information for research is very limited.
Just like other cancer problems, DIPG can develop when a person encounters a problem during the cell reproduction process in the body. It can also trigger the formation of other types of cancers due to its major central nervous system involvement.
Diagnosis
Treating DIPG in its first pace is the construction of a precise and complete diagnosis. The tumors are usually diagnosed through imaging studies.
Diagnostic steps usually start with:
- The physician conducts a full physical and medical examination of the patient
Other imaging tests are also possible such as:
- MRI for the image creations of detailed body structures and organs in the body
- Computerized tomography scan that involves computer technology
- X-rays to form cross-sectional photographs of the body
- Magnetic resonance spectroscopy which is done together with an MRI.
Organic compounds surrounding the tumor tissue can be cited as a way of identifying whether the tissue is normal or a tumor, and could possibly help if the tumor is glial tumor or if it originated in a neuron.
Treatment
Physicians usually base the course of treatment on several factors with a patient’s health status. Recommended treatments are intended to treat the tumor and for the symptoms.
Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy can help with the use of high-energy rays to shrink tumors and kill cancer cells. There are great responses in general, but it still does not improve survival rate since these responses are short-lived.
Biological and chemotherapy + radiation therapy
The biological and chemotherapy combined with radiation therapy have recently been conducted as treatment for the cancer.
Surgery is never an option for this condition since it can cause major neurological damage. Only biopsies are safely suggested.
Prognosis
Sadly, the prognosis for this disease is very poor since the removal of the tumor is too risky as it may lead to other serious complications. Studies show that the survival of some individuals is less than a year from the start of diagnosis.
The median overall survival of patients is ranging from 4-17 months. There are about 14-70% total of survival chance within a year, 0-25% chance at 2 years, and 0-10% at 3 years.
References
- Diffuse Intrinsic Pontine Glioma (DIPG) Symptoms, Diagnosis, Treatment, Surgery at http://weillcornellbrainandspine.org/condition/diffuse-intrinsic-pontine-glioma-dipg
- so much hope, so little support at http://www.thecurestartsnow.org/about/brain-cancer/dipg/
- http://www.danafarberbostonchildrens.org/conditions/brain-tumor/diffuse-pontine-glioma.aspx?__utma=98476749.1795290788.1444536303.1444536303.1444536303.1&__utmb=98476749.2.9.1444536369002&__utmc=98476749&__utmx=-&__utmz=98476749.1444536303.1.1.utmcsr=google|utmccn=(organic)|utmcmd=organic|utmctr=(not%20provided)&__utmv=-&__utmk=161262645&_ga=1.106606659.1795290788.1444536303
- Schroeder, K.M., Hoeman C.M., & Becher O.J (2014) . Children Are Not Just Little Adults: Recent Advances in Understanding of Diffuse Intrinsic Pontine Glioma Biology.”Pediatric Research 75(1), 205-09.
- Zaghloul MS, Eldebawy E, Ahmed S, Mousa AG, Amin A, Refaat A, Zaky I, Elkhateeb N, Sabry M (2014 Feb 20). Hypofractionated conformal radiotherapy for pediatric diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma (DIPG): A randomized controlled trial. Radiother Oncol.
- Donaldson, S.S., Laningham, F. & Fisher, P.G (2006). Advances toward an understanding of brainstem gliomas. J Clin Oncol 24, 1266-1272.
Similar Posts:
- Pineal Gland Tumor
- Aspartame Cancer
- Anaplastic Astrocytoma
- Medulloblastoma
- PNET Tumor
- Pineoblastoma
- Mast Cell Tumor






Leave a Reply